
 |
First Concepts.
WOB is Optimal
There are two
types of diabetes; juvenile, originating in insulin shortage, and adult diabetes, manifested by insulin
resistance. We shall
be concerned with the second, known as non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus.
Disease progression
Diabetes is a disease in which carbohydrate
metabolism is disturbed. It evolves along the following phases:
Pathogenesis
Diabetes results from a disturbed metabolism of carbohydrates. Carbohydrate
utilization is reduced. Lipid and protein utilization is increased. Blood sugar rises and is
spilled out into the urine. The body loses water and electrolytes and becomes
dehydrated. Diabetes progresses through two major phases : Primary, marked by hyperglycemia, and a secondary, during which blood vessel changes predominate.
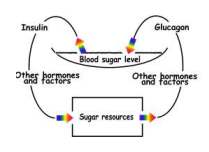
Blood glucose
level is controlled by two hormones,
insulin which removes glucose from the blood and stores it in tissues,
and glucagon, which mobilizes sugar into the blood. When blood glucose
rises (hyperglycemia), insulin increases glucose removal, glucagon reduces
glucose mobilization, until the original glucose level (normoglycemia) is
restored, and vice versa.
As diabetes evolves,
insulin becomes less effective in removing sugar from blood to tissues and blood glucose level
rises (hyperglycemia). Which is known as insulin resistance. Either tissue receptors become abnormal, and therefore take up less glucose, or
antibodies make insulin ineffective.
Secondary
diabetes
Hyperglycemia
damages walls of small
vessels which supply blood to tissues. Usually when a tissue requires more
resources, blood vessels dilate and bloodflow rises. Damaged blood vessel
walls become rigid, and fail to dilate when required, which leads to relative
resource shortage in tissues (ischemia). Many small blood vessels become obstructed
(micro-angiopathy)
and cells die (necrosis)
which is manifested by retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy.
Who is right,
Medicine or WOB?
The section on disease progression is a summary of the observed diabetes,
while Pathogenesis explains its behavior. If you have read the chapter 'WOB
is optimal',and accept its conclusions, you may feel somewhat uneasy.
Medicine presumes that diabetes is initiated by a random metabolic error,
loss of blood glucose control due to a malfunction of insulin. With
time, additional random errors aggravate the disease, and initiate secondary
changes. As this legend spreads, molecular biologists search for a mutated
gene, which makes insulin inefficient, and starts diabetes. Medicine believes
that all diseases are genetic, and start as gene mutations.
Yet this explanation
violates the principle of WOB optimality. While WOB secrets beat our understanding,
we can always rely upon its being
optimal! If it seems to us as if WOB erred, we got it all wrong since failing to grasp WOB sophistication.
WOB optimality is the corner stone of medical explanation.
Three precious
substances
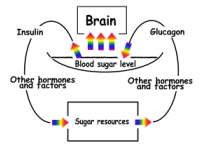
We start with
an anatomical observation, and ask which are the most important organs in our body? Obviously those who get the
biggest share of resources. Check organ blood supply and you will find that
the brain is the
most distinguished one. Then you may ask
what are the most precious
ingredients which the
brain requires? To find out, check which substances in the blood are under
the tightest control? Oxygen, glucose, and calcium. When one of them becomes scarce, brain
stops functioning and we faint.
Oxygen is monitored by a highly sensitive receptor
linked to the brain stem. When this precious gas becomes scarce, brain accelerates
respiration and heart rate, and if it fails we faint. Blood calcium level is controlled by the parathyroid
hormone. The blood provides calcium to all cells and particularly to the bone,
yet WOB is most obliged to the brain. When the brain requires more calcium
other cells get less, and the bone releases its own calcium. Glucose control is even tighter, since it is so
essential for the brain. It is controlled by several hormones , insulin, glucagon,
steroids, and others . All assure that the brain gets its major share.
Yet maintaining
an adequate blood concentration of these precious substances is not enough.
Blood flow through the brain has to be controlled as well, which is achieved
by controlling blood pressure. Elevated blood pressure raises blood
flow and vice versa. It is striking that our mouth is equipped with special
taste buds for sugar and salt. The latter is required for maintaining
an adequate blood pressure.
 |
New pathogenesis
Progression of
diabetes is driven by the brain's rising demand for glucose, which may be inferred from WOB behavior. Initially patient is unaware
of its elevated blood sugar. Since WOB is silent patient is healthy. As demand for glucose rises, blood glucose
rises too (hyperglycemia), reaching a threshold above which glucose is spilled
into the urine (glucosuria). Despite the waste of glucose, glucosuria is the most optimal (cheapest) way to maintain equilibrium, otherwise
patient might faint. Glucosuria leads to loss of fluid (polyuria), and WOB sends its first signals, like
thirst, meaning:" I am losing control
of water resources, get me some water". Mind obliges, yet soon it is
required to wake up several times during the night in order to pee and drink.
Patient becomes tired and worn out, turns to the
physician who finds that the urine is sweet.
 |
Diet
He first treats
hyperglycemia conservatively,
instructs the patient to avoid sugar, increase protein consumption, reduce
weight, and do some exercise. Hyperglycemia disappears and the patient feels
better, which shows that hyperglycemia can be treated as such. Blood sugar
drops since the body requires
less glucose, while brain gets its increasing share. Since the excessive brain
carving for sugar has not been curbed, patient has not been cured. Disease entered a remission, which is defined as lessening in
severity of the symptoms of a disease.
Since WOB is silent patient is healthy.
Exercise trains organs to utilize energy more efficiently. Weight reduction
eliminates glucose utilizing cells, which leaves more glucose for the brain
despite normoglycemia. As to the diet, if diabetes is driven by an increased
glucose demand by the brain, sugar restriction may not be advised Do not restrict
diet and let WOB select what it needs.
Insulin resistance
Since brain continues
being unsatisfied, disease progressed, and blood glucose rises. Medicine
blames this rise on insulin. Less insulin is produced (relative insulin
deficiency), and what is produced is deficient since it fails to lower blood glucose to
its 'normal' level. Diminished effectiveness of
insulin in lowering blood sugar
is called insulin resistance . Actually what insulin resists are the expectation of medicine, which attempts to lower blood glucose while WOB opposes it, and will make insulin even more resistant.
Further reading::
Four causes of daisese
How much insulin?
These arguments
have far reaching implications on treatment. Although WOB continues maintaining
an optimal equilibrium despite brain’s rising demands, the patient (mind)
suffers. He requires more and more fluid (liters), and spends sleepless nights
in the bathroom. Treatment has to establish a compromise between WOB and
patient (mind). Lowering
blood glucose will damage the brain, while leaving it high damages the patient.
One cannot fully satisfy the patient (mind) and lower blood sugar to normal
level since he will pass out.
Glucose level
set point
As diabetes evolves,
brain raises the blood glucose level set point, which indicates the glucose
level which for the brain is 'normal' or normoglycemic. The brain determines
what it regards as normoglycemia. Any blood glucose reduction below the
set point is regarded by the brain as hypoglycemia. Inflicting the same damage
to the brain like hypoglycemia in the non-diabetic.
The establishment
of a compromise blood sugar level is the major task of the physician, who
has to find out how to let the patient to enjoy life, while minimizing
his brain damage. Needless to say that medicine opposes
such views and requires to lower blood sugar level to ‘normal’
values, which is an example how treatment contradicts WOB requirements.
WOB controls cancer
While searching
for a compromise between WOB and Mind, physician can be assisted by an vital
WOB skill. WOB can be trained. Since (relative) hypoglycemia is a major
obstacle to an adequate therapy, why not train WOB (brain) to live with hypoglycemia
in peace? It is like training oneself to consume more
and more alcohol and remain sober. Initially small amounts of alcohol make
you drunk. As you drink more you gradually learn (get used) to remain sober
despite the quantity. In the same way WOB can be trained to handle any poison
or threat. This skill of WOB received in this site the Yogi suffix.
The same as the Hindu Yogi controls many unconscious and involuntary processes,
Poison-Yogi, handles excessive amounts of poison, and
so does Alcohol-Yogi. Insulin-Yogi,
'remains sober' despite excessive hypoglycemia.
'Remaining sober'
means that WOB does not complain, and therefore brain does not suffer from
hypoglycemia. Thus, treatment
of diabetes ought to be based on two (evolving) strategies, lowering hyperglycemia and WOB training.
Further reading
Cancer-Yogi
Cancer-Yogi-1
Cancer-Yogi-2
Iatrogenic medicine
Acute complications
In acute situations, like infection,
and keto-acidosis, insulin is life saving. Here medical treatment directives are clear
cut. However when the crisis is over, and disease proceeds an indolent course,
treatment directives are confused. This applies to all chronic diseases. While
medicine is extremely successful in treating acute conditions, it generally
fails in chronic disease, particularly in secondary diabetes, when treatment
is confined solely to insulin, and surgical repair of diabetic complications.
Yet much more can be undertaken than that.
Alternative
therapy
The
main therapeutic objectives, are to induce remission and/or slow down disease
progression, which can be achieved in two ways: 1. Utilize glucose more efficiently by tissues,
and 2. to divert more glucose to the brain.
Improved glucose utilization
-- Healthy eight hours natural sleep without pills. .Patient has to learn how to sleep
by himself and relax. Next comes meditation which ought to be practiced in
intervals throughout the day. Then come methods for reducing worries. The
patient is advised to learn these techniques from experts, and become independent.
-- Sport lowers blood sugar by utilizing
it more efficiently. Not only muscles, become more efficient but brain as
well. Efficiency means, that the same effort requires less breathing and slower
heart rate, two functions that require glucose. Exercise has to be gradual, since if exaggerated, sport
deprives glucose from the brain, and promotes diabetes. Medicine ought to realize
that these methods are as effective as insulin.
-- Some treatments known as Complementary
Alternative Medicine (CAM) promote more efficient glucose utilization.
Glucose
diversion to the brain.
-- By training tissues to utilize glucose more efficiently more glucose is
diverted to the brain.
-- However the most important way to save sugar is by reducing weight. Obesity is the main risk factor
for diabetes mellitus and is
nicknamed as diabesity The fat tissue competes
with the brain for the sugar, and promotes insulin resistance.
-- The design of an adequate diet is not at all simple, since excessive weight reduction
lowers blood glucose level, and may
harm the brain. Weight ought therefore be reduced gradually. Slim individuals do not require
any diet, since glucose restriction might harm the brain.
Then
comes hygiene which prevents undesired infections. It is not at all trivial. Some
soaps for instance weaken the skin barrier to microbes. One ought also
consider the skin and gut flora.
Further reading
Cancer and meditation
Microbe resistance
Essential
hypertension.
Diabetes and
essential hypertension have much in common. Medicine claims that in diabetes
the culprit is insulin, and that a flawed blood pressure control drives essential hypertension, which is called
‘The Silent Killer’. However,
the therapeutic objectives are the same: To induce remission and/or
slow down disease progression
Why
not assume that hypertension, like diabetes is driven by the brain? The above arguments may then be applied
also to hypertension. The major task of the physician is to establish a compromise blood pressure . Allowing the patient to enjoy life, while minimizing his brain damage.
Among other he will have to train the patient to become a Hypotension-Yogi.
Four causes of Disease
Etiology of disease
Cause and Etiology
An in depth study of Diabetes Mellitus
| Diabetes mellitus | Essential hypertension |
| Hyperglycemia | Hypertension |
| Loss of fluids and minerals | Fluid and salt retention |
| Blood vessel changes | Blood vessel changes |
| Increased susceptibility to infection | Increased susceptibility to infection |
| Diminished blood supply to tissues | Diminished blood supply to tissues |
|
Major complications |
Major complications Stroke, heart failure,and kidney failure, |